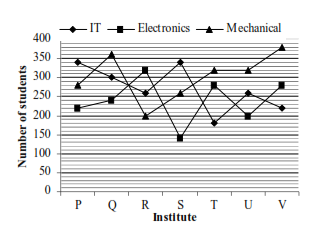
Directions (Q. 1-6): Study the following graph carefully to answer the given questions.
Strength of seven technology institutes with specialisation in IT, Electronics and Mechanical in 2012.
1. If the no. of students with Mechanical specialisation in each institute increased by 20% and the no. of students with Electronics specialisation in each institute decreased by 15% from 2012 to 2013, the total no. of students with Mechanical from all the institutes in 2013 is approximately what per cent of the total no. of students with Electronics specialisation from all the institutes in 2013?1) 122
2) 116
3) 162
4) 132
5) 178
2. What is the ratio of the total no. of students in institute R to that in V?
1) 39 : 43
2) 39 : 44
3) 37 : 44
4) 39 : 45
5) 38 : 43
3. What is the difference between the total no. of students with IT specialisation from all the institutes together and the total no. of students with Mechanical specialisation from all the institutes together?
1) 260
2) 240
3) 280
4) 220
5) 250
4. If the no. of students in institutes P, Q and R with IT specialisation increased by 15%, 22% and 10% respectively from 2012 to 2013, what was the total no. of students with IT specialisation in the three institutes together in 2013?
1) 1028
2) 1056
3) 1043
4) 1142
5) 1145
5. If out of the total no. of students for all three specialisations together in Institute Q, the no. of
students having liking for Music, Painting and Cricket are in the ratio of 5 : 6 : 7, then what is the no. of students having liking for Music from this institute?
1) 250
2) 300
3) 350
4) 360
5) 280
6. In institutes P, T and U the percentage of girls out of total no. of students with Electronics specialisation in the respective institutes is 50%, 55% and 48% respectively, what is the total no. boys in these three institutes with Electronics specialisation?
1) 340
2) 386
3) 356
4) 360
5) 314
Directions (Q. 7-12): Study the table and answer the given questions:
Advertisement revenues (in ` thousand) generated from Printed Version (PV) and Online Version (OV) of 6 magazines during 6 months
7. Which of the given statements is/are true?
(A) Total advertisement revenue generated from online version by magazine T in all the given months together is exactly 44% less than the total advertisement revenue generated from printed
version by the same magazine in all the given months together.
(B) The difference between advertisement revenue generated (from both online and printed version)
by all the given magazines in January and advertisement revenue generated (from both Online and Printed version) by all the given magazines in June is `62000.
(C) Only for one magazine the advertisement revenue generated from printed version displayed a
constant increase from the previous month during the given 6-month period.
1) Only (B) and (C)
2) Only (A) and (B)
3) Only (A)
4) Only (B)
5) All (A), (B) and (C)
8. Total advertisement revenue generated from online version by Magazine U in all the given months together is by what per cent more than the total advertisement revenue generated from printed version by the same magazine in all the given months together?
1) 25
2) 27.5
3) 35
4) 30
5) 32.5
9. In case of Magazine R, between which two given months was there approxi mately 15% rise in advertisement revenues generated (from both Printed and Online version together)?
1) January-February
2) February-March
3) May-June
4) March-April
5) April-May
10. The ratio of advertisement revenue generated from printed version by Magazine P to advertisement revenue generated from online version by the same magazine in July is the same as the ratio of advertisement revenue generated from printed version by Magazine Q to advertisement revenue generated from online version by the same magazine in March. If the advertisement revenue generated from online version by Magazine P in July was `1,08,000, what was the advertisement revenue generated from the printed version by the same magazine in July?
1) `1,87,000
2) `1,53,000
3) `1,36,000
4) `1,70,000
5) `1,19,000
11. What is the ratio of the total advertisement revenue generated from online version of all the given magazines together in February to the total advertisement revenue generated from printed version of all the given magazines together in May?
1) 33 : 28
2) 39 : 28
3) 27 : 16
4) 33 : 20
5) 27 : 22
12. The total advertisement revenue generated from printed version by Magazine P in January and April together is what per cent less than the total advertisement revenue generated from online version by magazine S in February and June together?
1) 22
2) 14
3) 27
4) 19
5) 17
Answer:-
1. (5); Total number of students with Mechanical specialisation in 2013 = 2544Total number of students with Electronics specialisation in 2013 = 1428
Reqd % = (2544 / 1428) * 100 = 178.15 = 178%
2. (2); Reqd ratio = 780 / 880 = 39 : 44
3. (4); Number of students with IT specialisation = 340 + 300 + 260 + 340 + 180 + 260 + 220 = 1900Number of students with Mechanical specialisation = 280 + 360 + 200 + 260 + 320 + 320 + 380 = 2120 Difference = 2120 – 1900 = 220
4. (3); Total number of students in Institutes P, Q and R with IT specialisation in 2013= 340/100 * 115 + 300/100 * 122 + 260/100 *110= 391 + 366 + 286 = 1043
5. (1); Total number of students in Institute Q = 240 + 300 + 360 = 900The number of students liking music from Institute Q = 900 * 5 / 18 =250
6. (1); The number of boys in Institutes P, T and U with Electronic specialisation = 340
7. (4); Check options one by one. (A) Total revenue generated from Online version by Magazine T = 209 + 217 + 185 +156 + 139 + 144 = `1050 thousand Total revenue generated form Printed version by Magazine T = 152 + 186 + 116 + 129 + 187 + 154 = `924 thousand Online version revenue is more than Printed version revenue. Thus, (A) is not true.(B) Total revenue generated by all the given magazines in January = 169 + 163 + 201 +145 + 136 + 141 + 209 + 168 + 152 + 209 + 131 + 184 = `2008 thousand = `2008000Total revenue generated by all the given magazines in June = 172 + 141 + 142 + 163+ 178 + 243 + 211 + 177 + 154 + 144 + 151 + 194 = 2070 ? Difference = 2070 – 2008 = 62 thousand = `62000. Hence, B is true.(C) Neither type of magazines shows constant increase in its revenue from previous month.Hence (C) is not true. Thus, only (B) is true.
8. (3);
Total revenue generated from Online version by Magazine U = 184 + 190 + 219 + 236 + 111 + 194 = `1134 thousand
Total revenue generated from Printed version by magazine U = 131 + 98 + 118 + 174 + 168 + 151 = `840 thousand
Reqd % = (1134 - 840) *100 / 840
9. (4); % rise from Jan to Feb (305-277) * 100 / 277 = 10.10%Similarly, Feb to Mar (326-305) * 100 / 305 = 6.88%March to April = (375-326)* 100 / 326 = 15%April to May = (405-375)*100 / 375 = 8%May to June = (421-405) *100 / 405 = 3.9%Hence the required answer is March to April.
10. (2); The ratio of revenue generated by Magazine P in July is same as the ratio of revenue generated by Q in March.Reqd ratio of Q from printed version to online version in March = 204 : 144 = 17 : 12Revenue generated by P in July from printed version = 108000*17/12 = 153000
11. (1); Reqd ratio = (171 + 139 + 149 + 223 + 217 + 190) : (113 + 128 + 196 + 132 + 187 + 168) = 1089 : 924 = 33 : 28
12. (5);
Total revenue generated from printed version by Magazine P in January and April = 169 + 163 = 332
Total revenue generated from Online version by magazine S in February and June = 223 + 177 = 400
Reqd % = (400-332)*100 / 400 = 17%
You might also like.